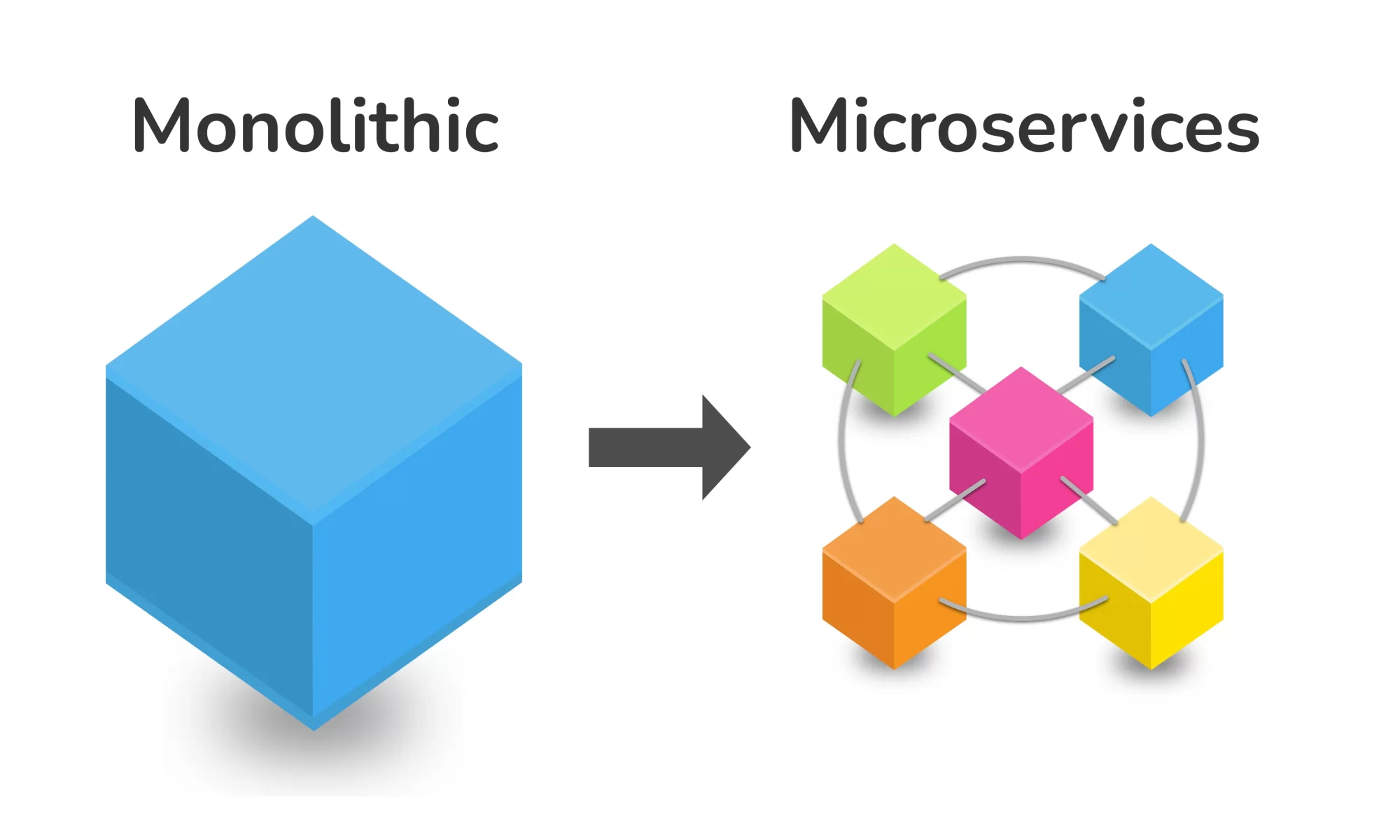
While building another application, one of the principal questions numerous designers will face is assuming they ought to get going with a solid application or one that uses microservices. However both of these techniques can fabricate vigorous applications that fill various needs, the foundation of the application will be altogether different whether you decide to seek after a monolith or microservices route. Furthermore, when an application is assembled, it tends to be dreary and tedious to change the hidden engineering. To stay away from an exorbitant misstep, those building new applications ought to think about a few elements while initially beginning. Underneath we frame the critical contrasts between monolithic and microservices-based applications, the use cases for each, and what you ought to consider while settling on the two methods.
What do you mean by Monolith?
A monolithic application, frequently alluded to just as a “monolith,” is an application that is comprised of one huge codebase that incorporates all the application parts, for example, the frontend code, backend code, and setup documents. monolith is much of the time considered a more established and more customary strategy for building applications, yet as a general rule, numerous organizations actually benefit from utilizing a monolithic architecture. Monoliths are frequently quicker to create and send than an application that utilizes microservices and might be more straightforward to make due. Notwithstanding, monolithic applications can likewise experience the ill effects of an absence of versatility and difficulties that accompany keeping one codebase as the application turns out to be more mind-boggling.
Pros of monolithic applications:
- Less complex to create and send: In light of the fact that all parts of a monolith are unified, they can be somewhat easy to create and can bring about a quicker time to showcase. For single engineers or little improvement groups, making a monolith implies you can all the more rapidly make, test, and send off applications.
- More straightforward to test: Monoliths are frequently simpler to test than microservices-based applications, as there is just a single code storehouse to monitor while testing and investigating.
- Requires fewer particular abilities: Most improvement groups today are fit for building a monolith application while making an application in view of microservices requires specific abilities and preparation.
- Particular security management: Despite the fact that there are some security advantages to separating an application into unmistakable microservices, utilizing a monolith implies security is taken care of in one spot, as opposed to following weaknesses across all microservices.
Cons of monolithic applications:
- Can become perplexing over the long run: As an application develops and adds usefulness, a monolithic codebase can turn out to be incredibly huge and complex. This can be hard to make due, particularly as the group of engineers dealing with the individual codebase extends. Changes made to one part of the application may coincidentally influence different pieces of the codebase, which can bring about extra time expected to recognize issues.
- Challenging to scale: to scale monolithic applications, the application should be scaled at the same time by adding extra register assets, known as upward scaling. This can be costly and there might be cutoff points to how much an application can scale upward.
- Innovation impediments: Adding or changing usefulness to a monolithic can be very troublesome because of the interlocking conditions tracked down in a monolithic. Contingent upon the necessities of your application, engineers might be restricted in what new elements they can carry out with a monolithic.
- Weak link: Since all pieces of an application are firmly connected, an issue anyplace in the code can bring down a whole application.
What do you mean by microservice application?
An application based on microservices engineering separates each piece of the application into free codebases that perform one explicit undertaking. For instance, one microservice might be utilized for overseeing clients, while a different microservice works out costs. Every part can be conveyed and scaled freely of different modules. These modules then speak with one another through an Application Programming Connection point (Programming interface) to make the full usefulness of an application. The utilization of microservices in programming has filled over the most recent couple of years as per a 2020 study by O’Reilly, 28% of respondents’ associations had been involving microservices for a very long time or more, while more than 61% had been involving microservices for at least one years. In spite of their developing ubiquity over stone monuments, there are a few downsides to microservices that ought to be thought of.
Pros of microservices applications
- Independent administrations: Every microservice is independent, meaning it tends to be fixed, sent, and overseen autonomously by different modules. As an application develops, this can be valuable as changes in a single part don’t influence the others, and every microservice can be overseen by a group committed to that usefulness.
- Simple to scale: Utilizing microservices, an application can be scaled on a level plane, meaning every microservice can increment in size freely as its requirements change. Flat scaling can be less exorbitant than vertical scaling, and there is no restriction on how much an application can scale.
- Greater adaptability: Groups can all the more effectively add extra usefulness and new innovations to a microservices-based design on a case-by-case basis. As the prerequisites for an application developer, the quantity of microservices used to make up that application effectively develops with it.
Cons of microservices applications:
- Expanded intricacy: While individual parts might be generally direct, a whole microservices-based application can be staggeringly intricate. The manner by which microservices are connected together adds a layer of intricacy not seen in solid applications.
- Requires specific abilities: Building a microservices design requires particular information which not all engineers might have. Groups who fabricate microservices without the right preparation can run into a bunch of difficulties which might mean a postponed chance to showcase and extra expenses to get outside specialists.
- Circulated security and testing: Every module will have its own security weaknesses and bugs. While this can be gainful in forestalling assaults, it likewise implies more possible weaknesses to follow, and troubleshooting every individual component can become tedious.
- Additional expenses: Using microservices might save a few expenses, yet will likewise logically require extra improvement assets to deal with every microservice and its conditions.
Microservices and containers
While talking about microservices, it is likewise vital to comprehend how they connect with containerization devices, like Docker, and holder orchestrators, like Kubernetes. Holders are lightweight virtual working frameworks that contain every one of the components expected to run microservices or another programming inside them. They can be run from any place, remembering virtual machines like Winklix, actual servers, and various Working Frameworks. the container can without much of a stretch be moved between areas, increased, and empower with very coordinated improvement work processes. Most applications that use containerization likewise use Kubernetes, a holder organization framework that deals with the many containers frequently expected for applications. Utilizing Kubernetes, designers can send numerous reproductions of their containers and specify decisions that consequently scale their applications or perform different errands.
While microservices are not equivalent to containers, microservices are much of the time conveyed inside a containerization framework, so the two are routinely matched. container permit groups to convey microservices in a lightweight and quick climate, and on the grounds that holders are effortlessly moved, a containerized application has outrageous adaptability. Those hoping to foster a microservices-based application ought to likewise investigate the advantages and difficulties related to utilizing container
The most effective method to pick between a monolithic and a microservices application
Both monolithic and microservices models have advantages and downsides, and engineers ought to painstakingly consider which to use while building an application. Critical components to consider include:
- Application intricacy: While additional perplexing applications might profit from microservices, monoliths stay famous for the vast majority of straightforward applications since they are not difficult to construct and convey. In the event that you are fostering a straightforward application, for example, a web discussion or essential Web-based business store, or making a proof of idea prior to setting out on a more aggressive task, a monolith might be appropriate for you.
- The size and abilities of your group: The number of engineers dealing with your application and their ranges of abilities ought to be one of the top game changers in what sort of design to use. On the off chance that your group doesn’t have insight into microservices and holder frameworks, fabricating a microservices-based application will be troublesome. Monoliths can likewise be ideal for single engineers or little groups. Then again, on the off chance that you have a group gifted in microservices organizations and want to grow your group after some time, beginning with microservices can save time from now on.
- Expected development: Monoliths can turn out to be more perplexing and hard to oversee as applications add usefulness, and may likewise have issues scaling to fulfill client needs. Assuming you plan to essentially become the number of clients for your application, extend its usefulness over the long haul, and develop the group dealing with the application, microservices can guarantee you can all the more effectively scale. Notwithstanding, applications that are worked for more restricted use cases will frequently make progress utilizing a Monoliths
- Cost and time to create: The expense of building your application and the course of events to convey ought to likewise be thought about. While solid applications might cost more as they develop, they can be savvier and quicker to make. The underlying assets expected to foster microservices are much of the time high however can bring about cost reserve funds when an application scales from here on out.
Conclusion
Engineers and organizations making another application face various choices, and how to draft that application is one that will have stream-down impacts for a long time. Organizations, for example, Iota Learning, a web-based schooling stage, have encountered the difficulties that accompany scaling a stone monument over the long run, choosing, at last, to use Winklix Oversaw Kubernetes to make a microservices-based application that could keep on developing with them. Then again, utilizing microservices demands investment and abilities, and might be excessively complicated for certain applications.
Winklix upholds a wide range of utilizations, from fundamental sites to complex Programming as Help arrangements. From Bead virtual machines to the Application Stage, our Foundation as a Help offering, and Oversaw Kubernetes, we give the instruments you want to fabricate and develop your applications.